Review article to treat obesity: Pathogenesis, Health Risks, and Emerging Management Strategies
Introduction
Obesity is a multifactorial chronic disease that has reached epidemic proportions globally. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes obesity as one of the most significant public health challenges of the 21st century, with projections suggesting that lifestyle diseases, including obesity, may account for 30% of global deaths by 2030. Characterized by excessive body fat accumulation, obesity increases the risk of numerous comorbidities such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, obstructive sleep apnea, musculoskeletal disorders, and various cancers.
Epidemiology and Health Risks of Obesity
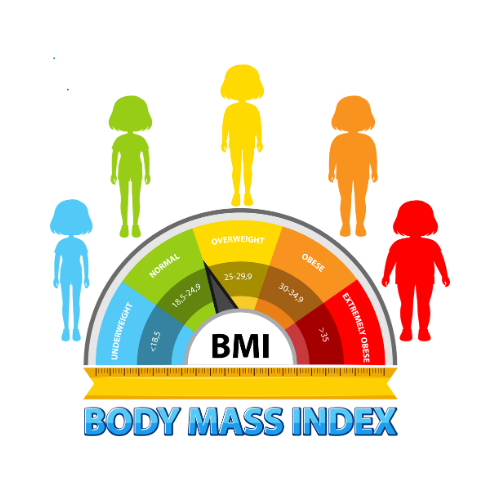
Recent statistics reveal that over one-third of U.S. adults are classified as obese, reflecting a troubling upward trend worldwide. Obesity is intricately linked to metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and certain cancers. The rising body mass index (BMI) among populations has led to a dramatic decline in life expectancy and overall quality of life.
Pathogenesis of Obesity: Biological and Environmental Factors
Obesity results from a complex interplay between genetic, epigenetic, environmental, and behavioral factors. The primary driver is a sustained energy imbalance between calories consumed and expended. Genetic predispositions, coupled with epigenetic modifications, influence individual susceptibility to weight gain. Furthermore, the social and physical environment, including diet patterns, sedentary lifestyle, and urbanization, plays a critical role.
Machine Learning in Obesity Prediction and Management
Advancements in technology have introduced machine learning (ML) as a promising tool in predicting obesity risk factors and managing overweight conditions. A systematic review identified 93 primary studies employing ML techniques between 2010 and 2020. These approaches enable early detection of obesity, offering accurate and immediate assessments of risk factors and guiding personalized interventions. Integrating ML can significantly enhance public health strategies and support clinical decision-making.
Therapeutic Interventions and Management Strategies
Managing obesity effectively requires a multifaceted approach. Evidence suggests that modest weight loss of 5-10% can significantly improve health outcomes. Interventions include dietary modifications, increased physical activity, behavioral therapy, pharmacotherapy, and surgical options for severe cases. Nurse practitioners and healthcare professionals play vital roles in setting realistic weight-loss targets, providing support, and monitoring progress.
A novel area of focus is intermittent fasting (IF), which has shown efficacy in reducing systolic and diastolic blood pressure, improving insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IR), and reducing triglyceride levels in overweight and obese individuals. A recent meta-analysis encompassing 15 studies with 929 participants confirmed that IF can substantially lower blood pressure and improve metabolic markers, with manageable and self-limiting side effects such as transient vomiting and irritability.
Obesity Research Networks and Future Directions
The American Heart Association’s Strategically Focused Research Network (SFRN) on Obesity has fostered significant advancements in understanding obesity mechanisms and developing therapeutic targets. Collaborations between leading institutions like Johns Hopkins, NYU, and Vanderbilt have propelled the field forward, bridging basic science with clinical applications.
Conclusion
Obesity is a complex condition necessitating comprehensive management strategies that address biological, behavioral, and environmental factors. Emerging technologies like machine learning and innovative interventions such as intermittent fasting provide new avenues for prevention and treatment. Continued research, public health initiatives, and personalized medical approaches are essential to curbing this global epidemic.
Emerging therapies for obesity are revolutionizing the way we approach weight management, offering hope to individuals who have struggled with traditional methods. As highlighted in the detailed insights shared by The Labon Emerging Therapies for Obesity, innovative interventions like pharmacotherapy, targeted biologics, and gut microbiota modulation are showing promise in tackling obesity’s complex root causes. These advancements, when combined with lifestyle interventions such as nutrition and exercise, present a more holistic and sustainable path for weight loss and metabolic health improvement.
For those seeking a structured and personalized approach, The Labon’s Weight Management solutions (https://thelabon.com/weight-management/) provide comprehensive guidance tailored to individual health profiles. Integrating emerging medical therapies with proven lifestyle strategies ensures not only effective weight reduction but also long-term health benefits, such as improved cardiovascular health and diabetes prevention. This integrated model is pivotal in addressing obesity as a multifaceted disease, paving the way for more effective and lasting outcomes.
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. WHO Fact Sheets.
- Smith KB, Smith MS. Obesity Statistics. Prim Care. 2016.
- Mechanick JI, et al. Cardiometabolic-Based Chronic Disease, Obesity, and Precision Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019.
- Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, et al. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994.
- American Heart Association. Strategically Focused Research Network on Obesity. 2017.
- Zhou W, et al. The role of machine learning in obesity prediction and prevention: A systematic review. Comput Biol Med. 2021.
- Pan B, et al. Intermittent fasting and its effect on blood pressure and cardiometabolic markers: A meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2024.